You or your relative or your friend might have had symptoms such chest pain, shortness of breath or dizziness. It is, therefore, necessary to be aware of the most common disease of the growing urban population, namely coronary artery Disease (CAD), its symptoms, risk factors and the procedures which are done to evaluate and treat the problem.
What is Coronary Artery Disease?
CAD occurs when the arteries surrounding your heart are hardened and narrowed due to deposition of ‘plaque’ on the inner walls. As the plaque increases in size, the lumen of these arteries get narrower, resulting in lesser blood flow and lesser oxygen supply to the heart.
Symptoms of CAD
The severity of symptoms varies from mild chest discomfort to a severe chest pain due to a heart attack. The most common symptoms are chest pain or discomfort, pain in one or both arms, jaw, neck, stomach, dizziness, sweating, palpitation or shortness of breath. In some patients, the first sign of CAD is a heart attack. A heart attack happens when a plaque in the coronary artery breaks apart resulting in clot formation which causes 100% block in the artery.
Risk factors for CAD
The risk factors for CAD are:
- A family history of premature heart disease
- Smoking High blood cholesterol
- High BP
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Stress
Diagnosis of CAD
If you have symptoms of CAD along with one or more of the risk factors, you should not neglect the symptom and it is advisable to get evaluated. You may have to undergo basic blood tests along with ECG, chest X-ray, and Echocardiogram. Your doctor might recommend a stress test (TMT) if indicated. If the stress test is positive, you will require coronary angiography study. Coronary Angiography is the ‘gold standard’ test to see exactly the site, severity and the number of blocks in the coronary arteries. Based on the results, the cardiologist may advise medical management, Angioplasty (PTCA) or Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG). In some cases, the cardiologist performs the PTCA procedure immediately the following angiogram to improve the blood flow the heart.
Angioplasty Procedure
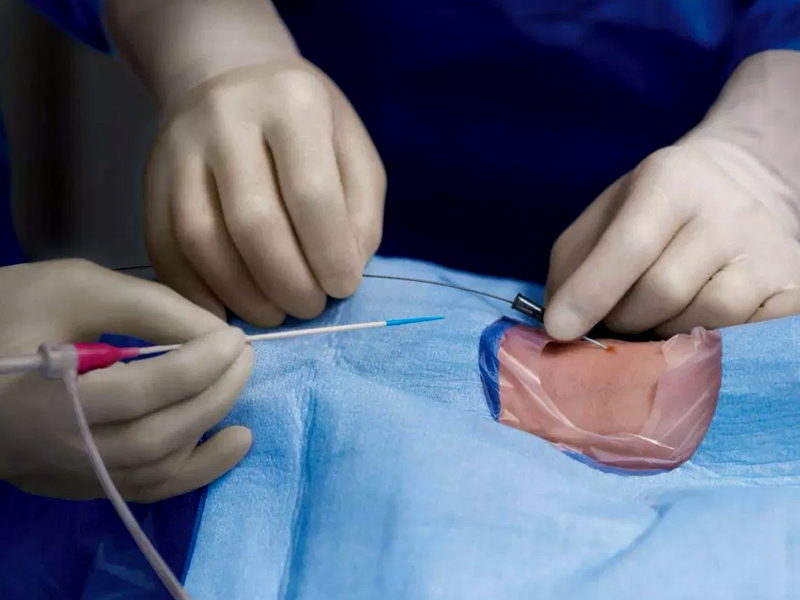
Angioplasty is performed in a cardiac catheterization laboratory (cath lab) It is done to reopen a blocked artery and restore blood flow to the heart muscle.
The Procedure
The patient is fully explained about the steps in the procedure. A needle puncture is made on the wrist or in the groin after injecting local anaesthetic drug. Then a sheath is inserted, through which flexible catheters are passed to the site of the blocked artery. The device (small balloon) is positioned at the end of
The special catheter and repeated inflations are done. The plaque is compressed against the walls of the artery and blood flow is restored. When the balloon is inflated, some patients might feel chest pain. This pain is temporary and the patient is advised to report to the doctor. The balloon is deflated and removed after opening the block.
What is a stent
A stent is a cylindrical wire mesh that is expandable which is crimped on the balloon. It is positioned at the site of the block just after balloon inflation. Inflation of the balloon deploys the stent at the site. This keeps the vessel open and maintains the blood flow.
What are the types of stent ?
A drug Eluting stent is coated with drugs to prevent re stenosis or recurrence. The drug eluted by the stent limits the growth of muscle cells in the vessel wall, reducing the chances of restenosis or reblockage.
What are the considerations in the postangioplasty period ?
After the procedure, the patient is shifted to the intensive coronary care unit and monitored. If the patient experiences any chest pain or discomfort, the nurse should be notified immediately. Patient is then shifted to his room the next day and is discharged in 2 days. Usually, patients can get back to their routine in a week’s time. But each patient is different and he/she will be advised during discharge by the doctor about the do’s and don’ts. regular follow up with the cardiologist, proper compliance with drugs, control of risk factors like Diabetes, lifestyle modification, diet adherence, refraining from smoking and alcohol on a whole will result in a good outcome for the patient.